Have you ever wondered how scientists make groundbreaking discoveries or how businesses make important decisions?
It all starts with research paper writing, but there isn't just one way to do it!
It can be confusing when you hear terms like "quantitative," "qualitative," or "basic" and "applied" research.
But don't worry, we're here to clear things up!
In this blog, we'll break down the different types of research, explain what each one means, and give you real-life examples for your better understanding.
So, get ready to find out how research impacts your studies!

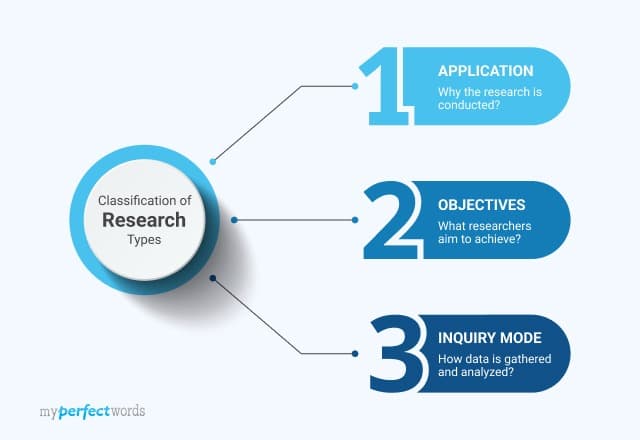
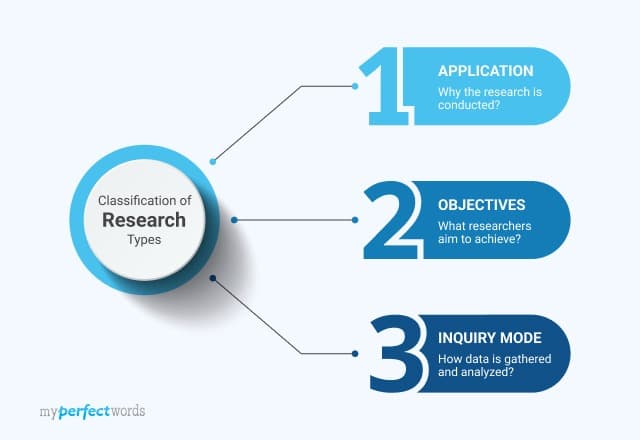
The following is a detailed description of these research types.
On This Page![]()
- 1. Fundamental Research
- 2. Applied Research
- 3. Qualitative Research
- 4. Quantitative Research
- 5. Mixed Research
- 6. Grounded Theory Research
- 7. Phenomenological Research
- 8. Survey Research
- 9. Action Research
- 10. Classification Research
- 11. Ethnographic Research
- 12. Deductive Research
- 13. Inductive Research
- 14. Field Research
- 15. Descriptive Research
- 16. Correlational Research
- 17. Exploratory Research
- 18. Explanatory Research
- 19. Longitudinal Research
- 20. Cross-Sectional Research
- 21. Policy-Oriented Research
- 22. Comparative Research
- 23. Causal Research
Fundamental Research
Fundamental research, often called basic research, is a crucial pillar of the research world. In this type of research, the focus is on expanding knowledge without a specific application in mind.
Fundamental research doesn't aim for practical solutions right away. It's about laying the groundwork for future breakthroughs.
It serves as the foundation for applied research, enabling innovations in technology, medicine, and more.
By pushing boundaries, fundamental research encourages innovation and pushes the frontiers of human knowledge.
Example:
James Clerk Maxwell's 19th-century work on electromagnetism, published in "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field," revolutionized physics and paved the way for modern telecommunications. Reference: Maxwell, J.C. (1865). "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field." Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. |
Applied Research
Applied research is the practical side of the research world, where knowledge is put into action. It's like taking a scientific concept and using it to solve real-world problems.
Unlike fundamental research, which explores the unknown, applied research aims for tangible results. It seeks to make an immediate impact on society, business, or technology.
Applied research spans various domains, including healthcare, engineering, agriculture, and economics. It addresses pressing challenges in each area.
Example:
The development of the polio vaccine by Jonas Salk in the mid-20th century is a remarkable instance of applied research. Salk's work, based on fundamental research on viruses, had a profound and immediate impact on public health. Reference: Salk, J. (1955). "Immunization against Poliomyelitis with a Vaccine Developed from the Virus of Human Poliomyelitis." Journal of the American Medical Association. |
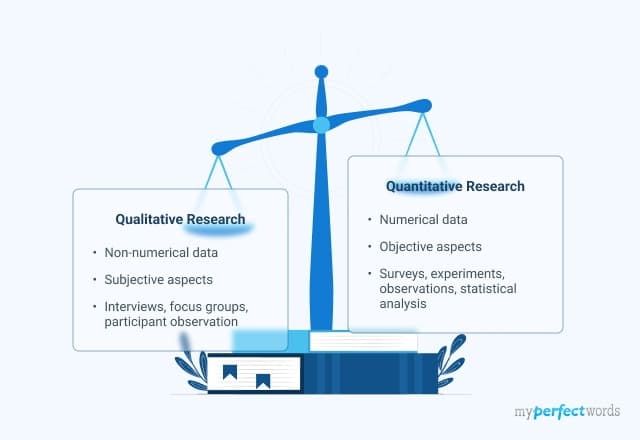
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a precise tool for understanding the complex details of human experiences. It explores words, meanings, emotions, gestures, and tone to find out hte outcomes.
This approach seeks to uncover richness through close observations and theoretical insights. It's about understanding what people feel without external influences clouding their perspectives.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative methods deal with non-numerical data.
Types of Qualitative Methods
Some famous types of qualitative research methods are:
- Case Study
- Focus Groups
- Text Analysis
- Ethnographic Studies
- One-to-One Interviews
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a systematic approach that places emphasis on factors such as generalizability, objectivity, and precision.
Quantitative research is characterized by its numerical orientation. It deals with data that can be measured and quantified.
It primarily deals with numeric data, aiming to answer questions related to the "what," "where," and "when" aspects of a phenomenon.
It establishes relationships between quantifiable data to control, predict, and explain a phenomenon. This data-driven approach aids in making precise predictions.
Types of Quantitative Methods
- Survey
- Description
- Correlation
Mixed Research
Mixed research is a comprehensive research approach that combines both qualitative and quantitative research methods within a single study.
It allows researchers to gather both numerical data and qualitative insights to gain a more holistic understanding of a research question.
Qualitative methods help explore the "why" and "how" of a phenomenon, while quantitative methods focus on the "what" and "how much."
Combining these approaches provides a more complete picture.
Example:
In education research, a mixed methods study might involve first conducting qualitative interviews with teachers to understand their teaching strategies. Then, a quantitative survey could be administered to a larger group of teachers to quantify the prevalence of these strategies. By combining both methods, researchers can explore the richness of teacher experiences and validate their findings with numerical data. Reference: Creswell, J. W., & Plano Clark, V. L. (2017). Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research. Sage Publications. |
Grounded Theory Research
Grounded theory research is a qualitative research method that aims to generate theories or explanations based on the systematic analysis of data.
The primary objective of grounded theory research is to develop theories that explain a phenomenon or social process. These theories are "grounded" in the data collected during the research.
Grounded theory follows an inductive approach, meaning that theories emerge from the data rather than being imposed on it.
Researchers systematically analyze data to identify patterns and concepts. They continuously compare new data with existing data, concepts, and categories to refine and develop their emerging theories.
Example:
In healthcare, grounded theory research has been used to explore the experiences of patients with chronic illnesses. Researchers might interview patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers, and then analyze the data to develop a theory that explains how individuals adapt to and manage chronic conditions. Reference: Charmaz, K. (2014). Constructing Grounded Theory (2nd ed.). Sage Publications. |
Phenomenological Research
Phenomenological research is a qualitative research method that focuses on exploring and understanding the lived experiences of individuals regarding a particular phenomenon or concept.
It is concerned with the subjective experiences of individuals, emphasizing their thoughts, feelings, and perceptions in relation to a specific phenomenon.
Researchers engage in a process known as "bracketing," wherein they temporarily set aside their own preconceptions and beliefs to approach the data with an open mind and without bias.
Example:
In psychology, phenomenological research has been used to explore the experience of grief among individuals who have lost a loved one. Researchers conduct interviews with bereaved individuals to understand their unique experiences, emotions, and coping mechanisms, contributing to a deeper understanding of the grieving process. Reference: Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological Research Methods. Sage Publications. |
Survey Research
Survey research is a quantitative research method that involves collecting data from a sample of individuals or entities through the administration of surveys or questionnaires.
It aims to systematically gather information about opinions, behaviors, attitudes, and demographics.
Surveys use structured questions and response options to gather standardized data from participants. This allows for easy comparison and analysis. Most survey questions have predetermined response options, often in the form of multiple-choice questions or rating scales.
Survey data is typically analyzed quantitatively using statistical methods to identify patterns, relationships, and trends.
Example:
In political science, survey research is widely used to gauge public opinion and voter preferences. Before elections, political organizations and researchers conduct surveys to understand which candidates are leading in the polls and to gather insights into voters' concerns and priorities. Reference: Fowler, F. J. (2013). Survey Research Methods (4th ed.). Sage Publications. |
Action Research
Action research is a dynamic and participatory approach to addressing real-world problems and driving improvement. It's a method that empowers individuals and organizations to make meaningful changes.
Think of action research as problem-solving in the moment. It's a proactive and practical approach that focuses on tackling specific challenges as they arise.
Action research involves close collaboration between researchers and practitioners. Together, they identify issues, develop interventions, and evaluate the outcomes of their actions.
Example:
In the field of education, action research is a valuable tool for teachers. For instance, a teacher might notice that some students struggle with a specific math concept. Through action research, the teacher can experiment with different teaching methods, assess their effectiveness, and adapt their approach based on the results. This ongoing process can lead to improved learning outcomes for students. Reference: McNiff, J., & Whitehead, J. (2011). All You Need to Know about Action Research. Sage. |
Classification Research
Classification research is a methodical approach to organizing and categorizing information, much like sorting items into different groups based on common characteristics.
It involves the systematic grouping of data, concepts, or objects into categories or classes based on shared attributes or criteria.
This method often employs qualitative techniques to categorize and describe data, such as content analysis or thematic coding.
Example:
In the field of library science, classification research plays a crucial role in organizing books and other materials in libraries. The Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC) system is a well-known example. Developed by Melvil Dewey in the late 19th century, this system assigns a unique numerical code to each book based on its subject matter. For instance, books on astronomy might be classified under the number 520, while books on history might have the number 900. Reference: Dewey, M. (1876). A Classification and Subject Index for Cataloguing and Arranging the Books and Pamphlets of a Library. Library Bureau. |
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is an immersive and in-depth approach to studying human cultures, societies, and communities. It involves researchers actively participating in and observing the daily lives and practices of the people they study.
The goal is to gain a holistic understanding of the culture, including its customs, traditions, beliefs, behaviors, and social structures. This often involves capturing not only what people say but also what they do.
Ethnographic research primarily relies on qualitative data, including field notes, interviews, and audiovisual materials, to document and analyze the culture under investigation.
Example:
In anthropology, ethnographic research has been used to study a wide range of communities and cultures worldwide. For instance, an ethnographer might live among a remote indigenous tribe for an extended period, documenting their daily life, rituals, and social interactions to understand their unique culture. Reference: Hammersley, M., & Atkinson, P. (2007). Ethnography: Principles in Practice (3rd ed.). Routledge. |
Deductive Research
Deductive research is a structured and methodical approach to investigation that involves testing a specific hypothesis or theory. It starts with a clear hypothesis or theory that the researcher wants to test or explore.
This type of research follows a structured and systematic process where researchers gather data, analyze it, and draw conclusions based on the initial hypothesis.
This method often relies on quantitative data and statistical analysis to draw objective and measurable conclusions.
Example:
In psychology, deductive research is commonly used to test theories or hypotheses about human behavior. For instance, a researcher may have a hypothesis that exposure to violent video games increases aggressive behavior in children. They would conduct experiments and analyze data to test and support this hypothesis. Reference: Anderson, C. A., & Dill, K. E. (2000). Video Games and Aggressive Thoughts, Feelings, and Behavior in the Laboratory and in Life. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78(4), 772-790. |
Inductive Research
Inductive research is a systematic approach to inquiry that involves generating theories, hypotheses, or general principles based on specific observations or patterns.
Inductive research begins with observations or specific instances and gradually builds to form broader theories or conclusions. Researchers adopt an open-minded and exploratory approach, allowing for unexpected findings and patterns to emerge from the data.
Unlike deductive research, which starts with a hypothesis and tests it, inductive research follows a bottom-up process, starting with specific data and moving toward generalizations.
Example:
In scientific research, Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection is a classic example of inductive reasoning. Darwin's observations of various species during his voyage on the HMS Beagle led him to develop the theory that species evolve over time through a process of natural selection. Reference: Darwin, C. (1859). On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. John Murray. |
Field Research
Field research is a methodological approach that involves gathering firsthand data and observations in the natural environment where a phenomenon occurs.
Field researchers venture into the field, which could be a physical location, community, organization, or any environment of interest, to collect data and gain insights. This approach often relies on direct observation of people, behaviors, events, or processes, allowing researchers to witness and record phenomena as they naturally unfold.
Qualitative and Quantitative: Field research can incorporate both qualitative methods (such as interviews and participant observation) and quantitative methods (like surveys or experiments) depending on the research objectives.
Example:
In anthropology, field research is a cornerstone of the discipline. Anthropologists may spend months or even years living among a particular community or culture, conducting participant observation, interviews, and ethnographic research to understand and document the way of life, beliefs, and practices of that group. Reference: Bernard, H. R. (2017). Research Methods in Anthropology: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches. Rowman & Littlefield. |
Descriptive Research
Descriptive research is a fundamental research method that involves the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data to provide a detailed picture of a specific phenomenon or topic.
This type of research is primarily concerned with observing and describing facts, characteristics, behaviors, or trends related to a particular subject or population.
Unlike experimental research, descriptive research does not involve manipulation or control of variables. It aims to depict reality as it is, without intervention.
Example:
In market research, descriptive research is frequently used to gather data about consumer preferences and behaviors. For instance, a company might conduct a survey to describe and understand how customers perceive their products, what features they value most, and how frequently they make purchases. Reference: Neuman, W. L. (2017). Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches. Pearson. |
Correlational Research
Correlational research is a systematic scientific method that aims to examine the relationship between two or more variables to determine if they are associated with each other.
This research is used to explore whether there is a connection or relationship between variables, but it doesn't imply causation. It helps us understand how changes in one variable might correspond to changes in another.
Correlations can be positive (both variables increase together), negative (one variable increases as the other decreases), or null (no significant relationship).
Example:
In psychology, a correlational study might examine the relationship between the amount of sleep a person gets and their academic performance. By analyzing data from a group of students, researchers can determine if there's a correlation between the two variables, helping educators understand the impact of sleep on student success. Reference: Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research Methods in Education. Routledge. |
Exploratory Research
Exploratory research is a flexible and open-ended approach to investigation, primarily used to gain a deeper understanding of a subject, phenomenon, or problem.
This type of research is conducted when the topic is relatively uncharted, and there's a need to form initial insights, ideas, or hypotheses. It often involves unstructured methods such as interviews, focus groups, or open-ended surveys, allowing for a more informal and fluid approach to data collection.
One of the key goals of this research is to generate ideas, theories, or hypotheses that can guide more structured research in the future.
Example:
In the business world, exploratory research is often used when a company is considering entering a new market. Initial research may involve open discussions with potential customers, suppliers, and local experts to gain a preliminary understanding of market dynamics, potential challenges, and opportunities. Reference: Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. Sage Publications. |
Explanatory Research
Explanatory research is a research method aimed at understanding the causal relationships between variables and explaining why certain events or phenomena occur.
Researchers often start with a hypothesis or a theory and use data analysis to test it. They examine the relationships between variables to see if the proposed causal links hold.
Explanatory research primarily employs quantitative methods, such as experiments, surveys, or statistical analysis, to identify and explain causal relationships.
Example:
In medical research, explanatory research may focus on understanding the reasons behind a particular disease outbreak. Researchers might investigate the potential causes, such as environmental factors or genetic predispositions, to explain why certain individuals are more susceptible to the disease. Reference: Trochim, W. M., & Donnelly, J. P. (2006). The Research Methods Knowledge Base (3rd ed.). Atomic Dog. |
Longitudinal Research
Longitudinal research involves the collection of data at multiple points in time. It is often used in developmental studies.
The significance of longitudinal research lies in:
- Measuring change over time.
- Testing causality.
- Establishing reliability and validity of measurement across time.
This type of research employs data collection methods, including personal interviews, surveys, archival records, or observations. It can also be a mixed-method involving more than one type of data collection method to achieve different goals.
Longitudinal research may take three different forms:
- Panel Study - It traces the same sample
- Cohort Study - It looks at a subpopulation over time.
- Trend Study - It analyzes the characteristics of a population over time.
Example:
In psychology and developmental research, longitudinal studies are commonly used to examine human development across the lifespan. Researchers may follow a group of individuals from childhood into adulthood, collecting data at various intervals to understand cognitive, emotional, and social changes over time. Reference: Bornstein, M. H., & Lamb, M. E. (Eds.). (2019). Developmental Science: An Advanced Textbook. Psychology Press. |
Cross-Sectional Research
Cross-sectional research is a methodological approach that examines a specific group of subjects or entities at a single point in time. This type of research captures data from a diverse group of subjects or entities at one specific moment, allowing for a snapshot view of their characteristics, behaviors, or attitudes.
Researchers can use cross-sectional studies to gather information from a wide range of individuals, organizations, or populations, providing insights into various aspects of interest.
While cross-sectional research offers valuable insights, it does not provide information about changes or developments over time.
Example:
In healthcare, cross-sectional research is often used to assess the prevalence of specific health conditions or behaviors within a population. For instance, a cross-sectional study might examine the rates of smoking among adults in a particular region at a specific point in time, providing insights into the current state of smoking prevalence. Reference: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2018). Current Cigarette Smoking Among Adults in the United States. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. |
Policy-Oriented Research
Policy-oriented research is a methodological approach that focuses on generating information, evidence, and insights to inform the development, implementation, and evaluation of public policies.
The primary goal of policy-oriented research is to provide policymakers with data, analysis, and recommendations that support informed and evidence-based decision-making.
It addresses pressing societal issues and challenges, such as healthcare, education, environmental conservation, and social welfare, to guide policymakers in designing effective policies.
Example:
In environmental policy, research on climate change impacts and mitigation strategies informs governments and international organizations about the necessity of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Such research contributes to the development of policies and agreements like the Paris Agreement, aimed at addressing climate change on a global scale. Reference: Weiss, C. H. (1979). The Many Meanings of Research Utilization. Public Administration Review, 39(5), 426-431. |
Comparative Research
Comparative research is an approach that involves examining similarities and differences between two or more subjects, ideas, or entities. It focuses on contrasting and comparing various aspects of subjects to identify patterns, trends, and variations.
This approach is versatile and can be applied to various fields, from sociology and economics to politics and literature.
Researchers can employ both qualitative and quantitative methods in comparative research, depending on their research questions and objectives.
Example:
In the field of economics, comparative research is frequently used to study the economic development of countries. Researchers may compare the economic policies, growth rates, and income distribution of multiple nations to understand the factors influencing economic success or disparities. Reference: Sachs, J. D., & Warner, A. M. (1995). Economic Reform and the Process of Global Integration. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity. |
Causal Research
Causal research is also known as cause-and-effect research. It is all about figuring out why things happen. It's like being a detective in the world of research, where researchers try to find out what causes certain outcomes.
Causal research helps us understand if changes in one thing cause changes in another. It's like asking, "Does doing this make that happen?"
Researchers often use experiments where they change one thing (called the independent variable) to see how it affects something else (called the dependent variable).
Example:
In medicine, causal research helps us understand if a new medicine really works. Imagine a study where doctors give a new drug to some patients and not to others. By comparing the outcomes, they can figure out if the drug is causing the improvement in patients' health. Reference: Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2001). Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs for Generalized Causal Inference. Houghton Mifflin. |
All in all, these are the types of research for both scientific and non-scientific academic fields.
Research is required to find causes, answers, and applications for underlying issues. This is because new processes, phenomena, events, and problems occur every day in our life, and we need practical and implementable solutions to tackle those problems.
If you have any difficulty choosing the type of research, you can get help from our professional writers. We understand that research paper writing is a daunting task, and not every student can write a good paper.
Worry not! MyPerfectWords.com is here to help you with all your writing worries.
Trust us for your 'do my paper' requests at affordable prices. So, you can always reach out to us for your papers and get a flawless writing piece within the given deadline.
Contact us to buy research paper online from experts today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is The Most Effective Type of Research Question?
The most effective research question is clear, specific, and relevant to the study's goals while also being feasible, testable, and grounded in theory.
It should address an ethical issue, hold interest and significance, remain open-ended, and align with the chosen research design.
What Type Of Research Source Provides The Best Firsthand Information?
Primary sources, such as original research studies, interviews, and firsthand observations, provide the best firsthand information, offering direct and unmediated insights into a subject.
Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!
Use our AI tool to generate high quality essay
WRITTEN BY
Alexander P.
Harvard Law graduate. I build arguments anticipating every objection and dismantling it before it's raised. Airtight logic is non-negotiable.
Keep reading
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples: Free Samples & Templates for Students

Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline

A Catalog of 300+ Research Paper Topics
-9352.jpg&w=828&q=75&dpl=dpl_Gdsvp7W41w43ZdA5Qu4MrGDa9Trz)
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide

How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
-9374.jpg&w=828&q=75&dpl=dpl_Gdsvp7W41w43ZdA5Qu4MrGDa9Trz)
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples

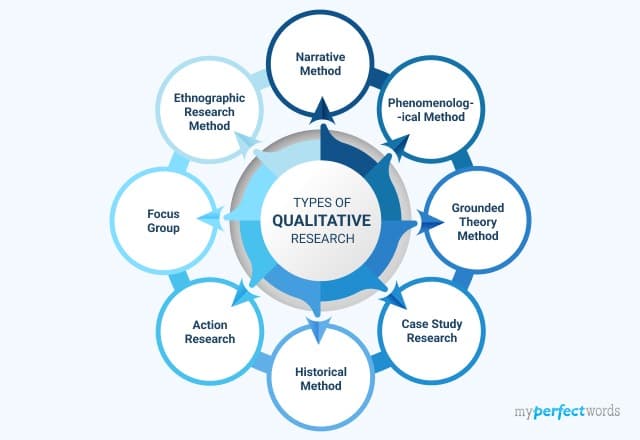
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2025
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques

230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide

Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas

A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples

Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide

How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips

How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples

Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide

Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2025)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2025 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2025
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper

